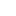
Seoul:The Capital of South Korea
Seoul is the capital city of South Korea and one of its most prominent cities in terms of size and importance. As the political, economic, cultural, and transportation hub of the country, Seoul plays a crucial role in shaping the nation's future.
Historical Background
Seoul has a rich history that dates back over 2,500 years to the Silla Kingdom era. It was established as a small fishing village called "Suwon" during the Three Kingdoms period. Over time, it became an important trading center due to its strategic location at the confluence of two major rivers—the Han River and the Geumcheon Stream—which facilitated trade with neighboring regions.
During the Joseon Dynasty, Seoul experienced significant growth, becoming a bustling metropolis known for its arts, culture, and commerce. The city's influence extended beyond Korea, attracting scholars and artists from across East Asia. This period saw the construction of numerous palaces and temples, which still stand today, serving as landmarks in modern-day Seoul.
Modern Development
The late 19th century marked a turning point in Seoul’s development when Japan annexed Korea under the rule of the Empire of Japan. This period introduced new architectural styles and infrastructure, including railroads and telegraph lines, transforming Seoul into a more centralized urban area.
In the early 20th century, after World War II, Seoul faced challenges like reconstruction and rebuilding following the devastating Korean War (1950-1953). However, post-war recovery efforts led to rapid economic growth, fueled by industrialization and investment in infrastructure. This phase contributed significantly to Seoul’s transformation into what it is today—a dynamic and cosmopolitan city.
Cultural Hub
Seoul remains a vibrant cultural center, boasting world-renowned museums such as the National Museum of Korea, the National Palace Museum of Korea, and the Gyeongbokgung Palace, which is one of the largest royal palaces in the world. Additionally, the city hosts various festivals throughout the year, celebrating traditional Korean customs and arts.
Economic Vitality
As South Korea's economic powerhouse, Seoul serves as the primary business district, home to many multinational corporations and international organizations. Its status as a global financial center is underscored by the presence of major banks, stock exchanges, and corporate headquarters. Seoul’s economy also relies heavily on technology, particularly in areas like IT services and digital finance, making it a leading player in the global tech industry.
Transportation Networks
Seoul’s comprehensive transportation network includes efficient public transit systems like the Seoul Metropolitan Subway and buses, along with highways and airports. These networks facilitate easy movement within the city and to other parts of South Korea. The Incheon International Airport, located just outside the city limits, serves millions of passengers annually, contributing significantly to Seoul’s tourism and logistics sectors.
Environmental Challenges
Despite its progress, Seoul faces environmental challenges such as air pollution due to heavy traffic and industrial activities. Addressing these issues is a critical part of Seoul’s long-term sustainability strategy. Efforts include promoting green initiatives, investing in renewable energy sources, and implementing stricter emission regulations.
Conclusion
Seoul, with its rich historical heritage and current economic vitality, continues to be an essential city in both South Korea and globally. Its position as the capital of a rapidly growing Asian power underscores its significance not only as a cultural and economic center but also as a model for sustainable urban development. As Seoul evolves, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the region’s future.

 上一篇
上一篇